- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Internet & the Web»
- Search Engines
How to search in google effectively?
Google is clearly the best general-purpose search engine on the Web.But most people don't use it to its best advantage. Using a special syntax is a way to tell Google that you want to restrict your searches to certain elements or characteristics of Web pages. Google has a fairly complete list of its syntax elements in its help page.
The first step is to narrow your search by adding search words.Google automatically searches for variations of the words you use. So, narrow it down to only pages with the exact phrase.Similarly, if you had results you wanted to exclude, you could use a minus sign on the page. Make sure you put a space before the minus sign and no space between the minus sign and the word or phrase you wish to exclude. Google automatically ignores many common words, such as "and," "or," "of," "a," etc. It also ignores some single digits or letters. This is usually not a bad thing, because the common words would just slow searches down without improving your results.
Occasionally it might be important to include one of these words in your search results. There are two ways to do this. One technique is to use quotation marks. Anything inside quotation marks is automatically included in the search, and the search will include the exact phrase.Another way to force common words in your searches is with the plus sign. Make sure that you do put a space before the plus sign and do not put a space between the plus sign and the search word you want to include.
When you put a tilde ~ in front of your search term, Google will look for both your chosen search term and synonyms. Do not put a space between the tilde and your search term. You may search for as many at once as you wish. Just put a tilde in front of every term you'd like to include. Google suggests, for instance, searching for ~food ~facts for information on recipes and nutrition. Either of those terms could be used, so how about searching for both of them at once? To find results that include either one term or another, type uppercase OR between the two terms you want to find
Google indents pages that are on the same website as the first result. This gives you a visual clue that you're looking at the same website. If you're looking for a specific piece of information, sometimes it can get buried in a long web page. Click on the Cached link, and Google will show you the snapshot of the webpage that is stored on their server with your keywords highlighted. This can help you scan a web page quickly to determine if it's what you need. Google can help with all sorts of advanced searches. Be sure to check the links at the top of the Google page to see if there's a search that might be more helpful or press the more button for more options.
Here are some advanced operators that can help narrow down your search results.
Intitle: at the beginning of a query word or phrase (intitle:"Three Blind Mice") restricts your search results to just the titles of Web pages.
Intext: does the opposite of intitle:, searching only the body text, ignoring titles, links, and so forth. Intext: is perfect when what you're searching for might commonly appear in URLs. If you're looking for the term HTML, for example, and you don't want to get results such as www.mysite.com/index.html, you can enter intext:html.
Link: lets you see which pages are linking to your Web page or to another page you're interested in. For example, try typing in link:http://www.pcmag.com.
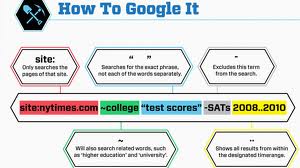
Try using site: (which restricts results to top-level domains) with intitle: to find certain types of pages. For example, get scholarly pages about Mark Twain by searching for intitle:"Mark Twain"site:edu. Experiment with mixing various elements; you'll develop several strategies for finding the stuff you want more effectively. The site: command is very helpful as an alternative to the mediocre search engines built into many sites.
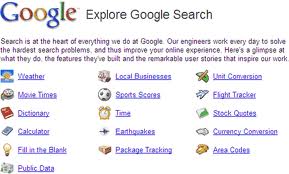
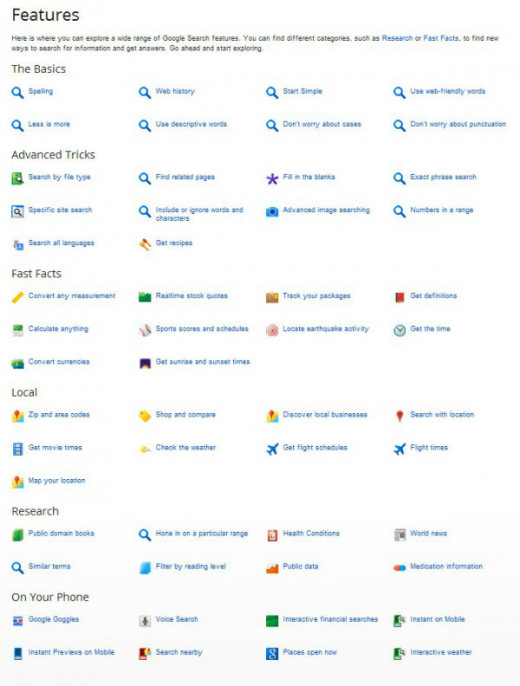
Google has a number of services that can help you accomplish tasks you may never have thought to use Google for. For example, the new calculator feature (www.google.com/help/features.html/calculator) lets you do both math and a variety of conversions from the search box.
You can restrict your searches to pages that were indexed within a certain time period. Daterange: searches by when Google indexed a page, not when the page itself was created.
Google can find web pages, images, maps and more. Explore some of the more interesting ways you can Google. Click on the images link in a Google web search to find pictures and graphic files that match your search keywords.Use Google Groups to search for posts on public Google Groups forums. Google News lets you search for your keywords in news articles from various sources. Use Froogle to search for products or services.Catalogs (http://catalogs.google.com), which features products from more 6,000 paper catalogs in a searchable index. And this only scratches the surface. You can get a complete list of Google's tools and services at www.google.com/options/index.html.
The complete list of features offered by Google is available at http://www.google.com/support/enterprise/static/postini/docs/admin/en/auth_ref/features_list.html.
Google goes far beyond a regular search engine. Give the tricks in this article a try. You'll be amazed at how many different ways Google can improve your Internet searching.